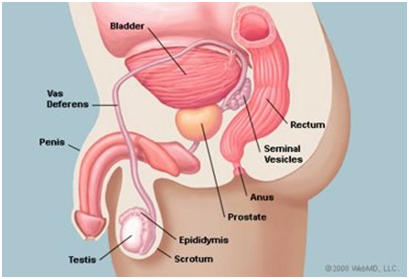
Looking for the best urologist in Dubai? Dr. Sanjay Bhat Hatangadi is a highly accomplished urologist, with over thirty years of experience in the field. He is widely recognized for his expertise in urology and has been associated with some of the most prestigious medical institutions in India and the Middle East.

Dr. Sanjay Bhat Hatangadi is an experienced urologist who has worked in various hospitals across India and Dubai. He served as the Professor and Head of Urology at Rajagiri Hospital and Amrita Medical College in Kerala from 2001 to 2019, where he supervised the urology department and provided training to new urologists.
During his tenure, he participated in multiple research projects and published numerous articles in peer-reviewed journals. After leaving Rajagiri Hospital, he joined Prime Hospital Dubai as the Head of Urology, where he managed a team of urologists and the hospital’s urology department until March 2022. His leadership skills and expertise in urology played a crucial role in the growth and development of the department. Currently, Dr. Sanjay Bhat holds the position of Consultant Urologist at Al Zahra Private Hospital Dubai. In this capacity, he provides expert advice and treatment to patients with complex urological problems.
His areas of specialization include Adult and Pediatric Laparoscopic and Reconstructive Urology/Uro-oncology, Prostate Disease Management, Stone Disease Management, Upper and Lower Urinary Tract Endourology, Incontinence and Female Urology, and Adrenal Surgery Laparoscopic. Dr. Sanjay Bhat Hatangadi is fluent in multiple languages, including English, Hindi, Kannada, Malayalam, Tamil, Konkani, and has a basic understanding of Arabic with a focus on urology-related terminology. This enables him to communicate effectively with patients from diverse backgrounds and provide personalized care.
Dr. Sanjay Bhat Hatangadi holds several qualifications, including MBBS, MS General Surgery, DNB General Surgery, FRCS General Surgery, MCh Urology, and FAGE Medical Education. He has published 41 articles in peer-reviewed journals and has received various awards, including the Best Outgoing Medical Student in 1987, the BS Sen Gold Medal for General Surgery, and the Howard Eddy Gold Medal for Royal Australasian College of Surgeons FRACS Part-1 South East Asia.
Looking for the best urologist in Dubai? Dr. Sanjay Bhat Hatangadi is a member of several professional organizations, including the Urological Society of India, Association of Southern Urologists, Urology Association of Kerala, and Emirates Urology Association. He continues to attend conferences and workshops to stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in his field.
Dr. Sanjay Bhat Hatangadi is available for full-time consultations at Al Zahra Hospital, Al Barsha 1, Dubai. He has held various academic positions, including Assistant Professor Urology at KMC Hospital Manipal, India, Registrar Urology at Armed Forces Hospital Oman, Professor Urology at Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences and Rajagiri Hospital, Kerala, India, and Consultant Urology at Prime Hospital Dubai. With his extensive experience, vast knowledge, and compassionate approach, he is one of the most sought-after urologists in the region.